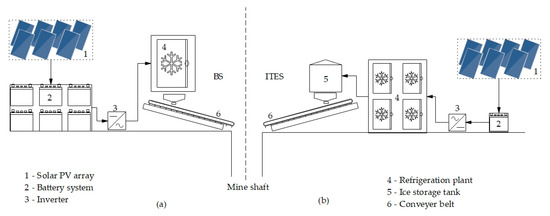
Ice Thermal Energy Storage Applications
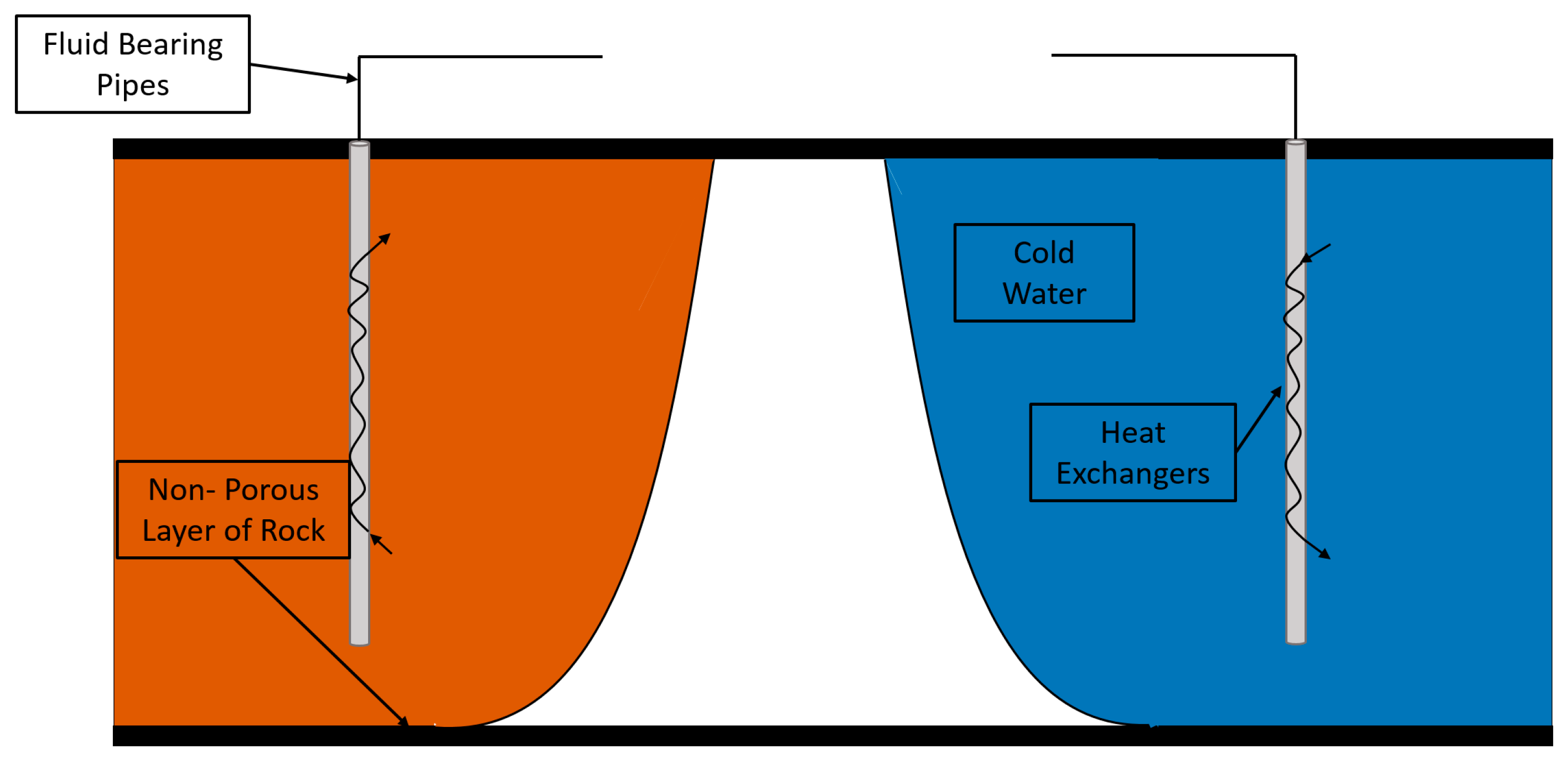
District heating non residential buildings industrial processes and power plants.
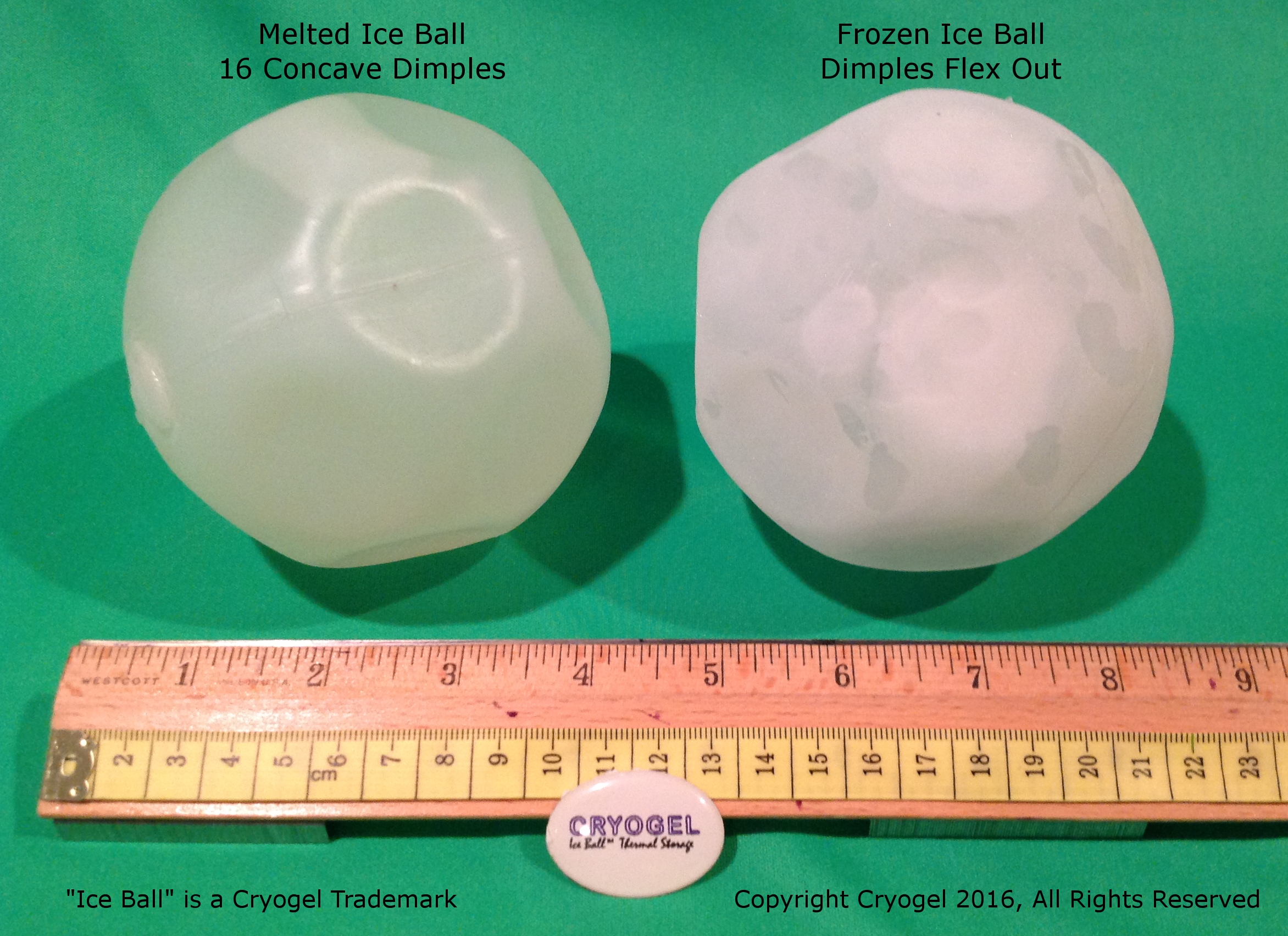
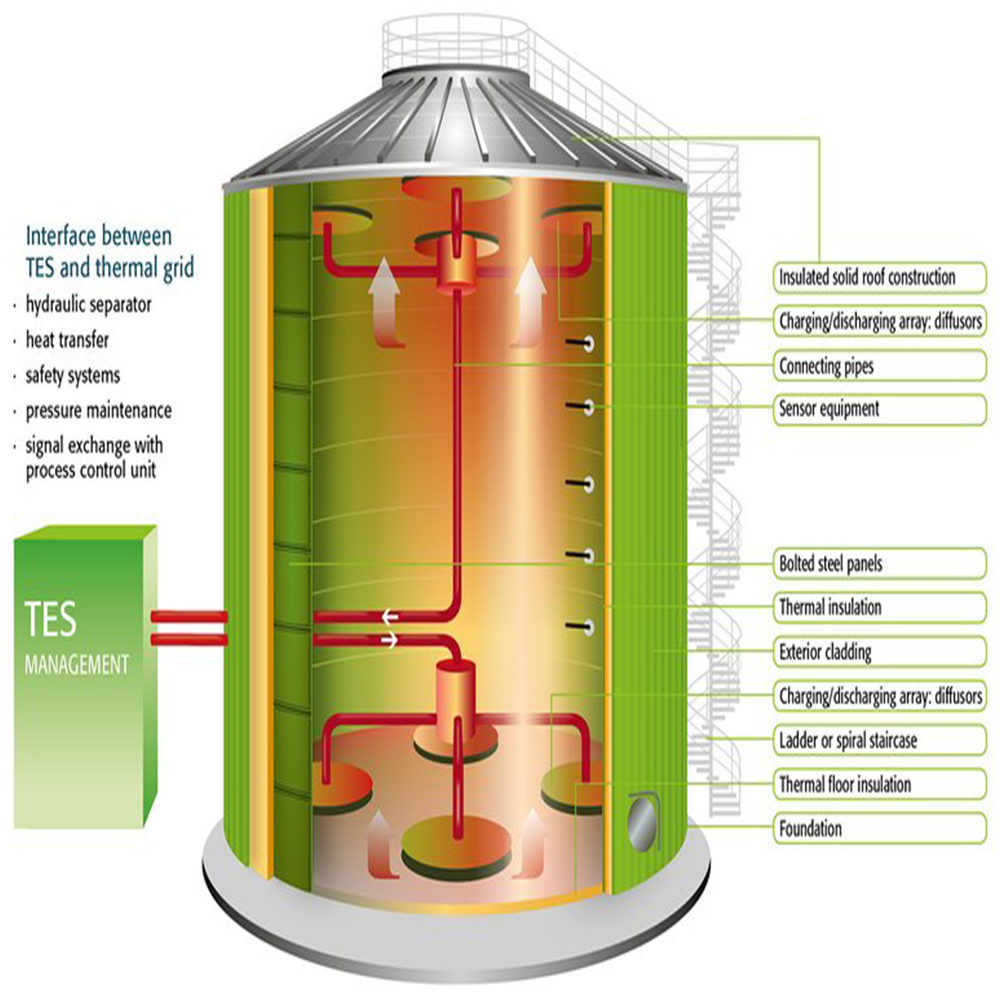
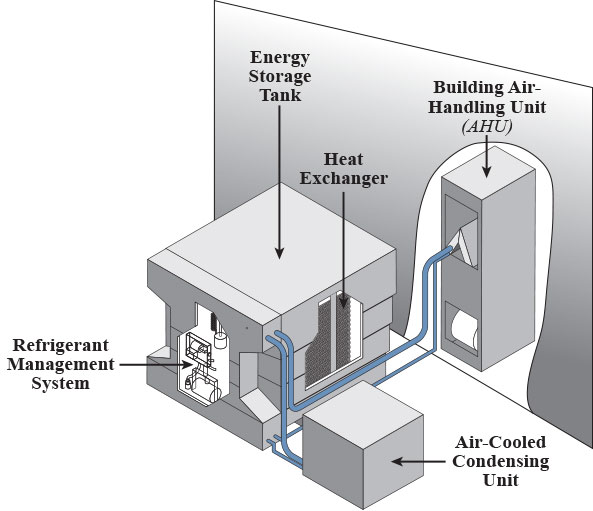
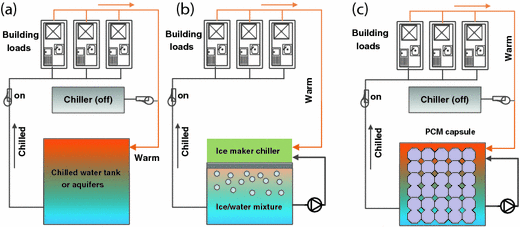
Ice thermal energy storage applications. Liquid air energy storage using liquefied air to create a potent energy reserve. Tesss are technologies that store thermal energy by heating or cooling a storage medium so that the stored energy can be used later for heating and cooling applications. Thermal energy storage is needed to improve the efficiency of solar thermal energy applications stea and to eliminate the mismatch between energy supply and energy demand. Block ice photo 1 was initially used for cooling in theaters where a 4 ft 4 ft 2 ft 1 22 m 1 22 m 0 61 m slab of ice would weigh 1 ton 907 kg and with the heat of fusion of 144 btu lb 907 kg would provide 12 000 btu h 334 kj kg over 24 hours hence our industry terminology.
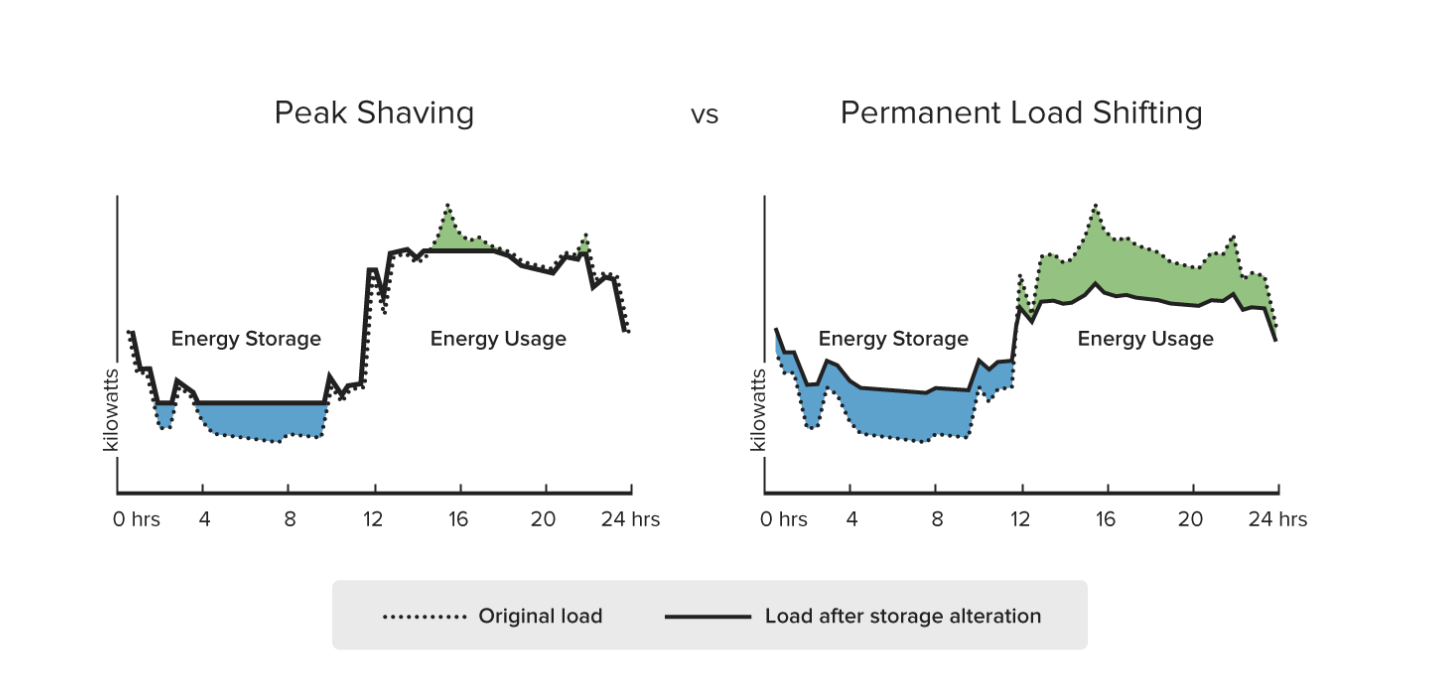
Btm thermal energy storage systems tesss are emerging as an important technology that can provide cost and energy savings for system owners and the power grid. One metric ton of water one cubic meter can store 334 million joules mj or 317 000 btus 93kwh. Thermal energy storage using ice makes use of the large heat of fusion of water. Concisely overview the state of the art benchmarks in some of the most tes relevant sectors.
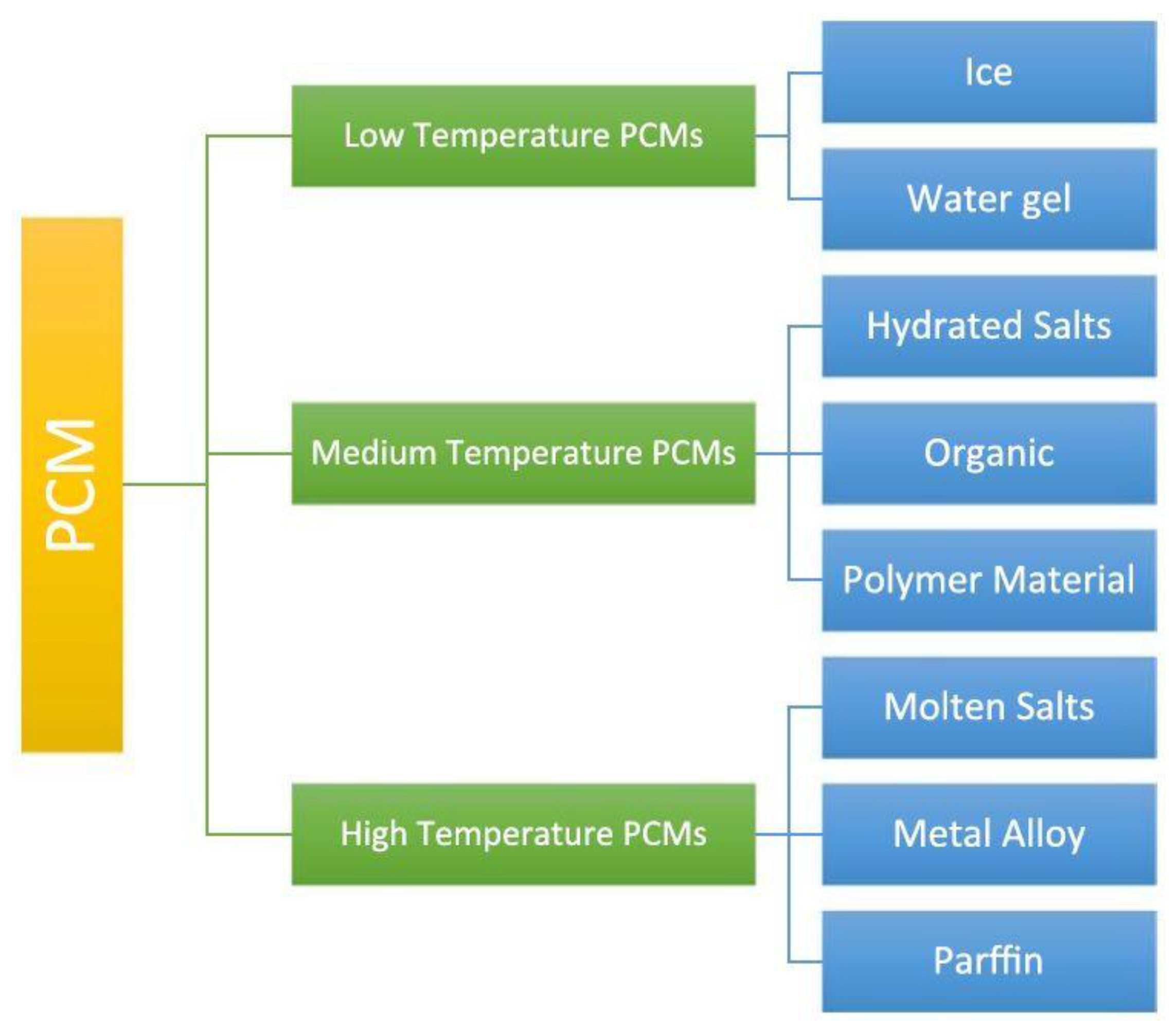
Among the thermal energy storages the latent. Tes systems are used particularly in buildings and industrial processes. Historically ice was transported from mountains to cities for use as a coolant. In this particular chapter we deal with a wide range of thermal energy storage tes applications from residential sector to power generation plants.
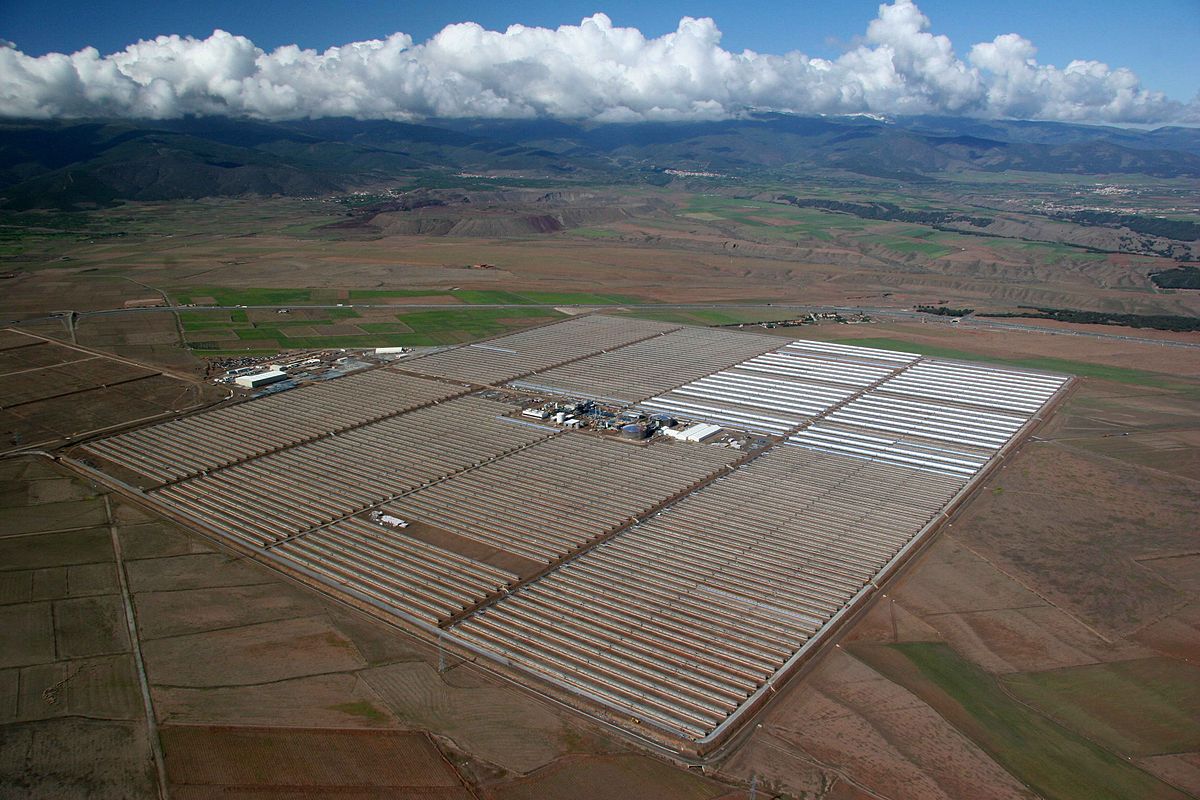
Liquid air energy storage laes uses electricity to cool air until it liquefies stores the liquid air in a tank brings the liquid air back to a gaseous state by exposure to ambient air or with waste heat from an industrial process and uses that gas to turn a turbine and generate electricity. Some practical applications of sensible heat and. Thermal energy storage tes is a technology that stocks thermal energy by heating or cooling a storage medium so that the stored energy can be used at a later time for heating and cooling applications and power generation.